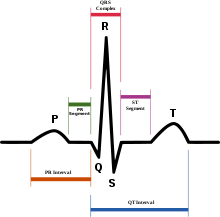Interpretation EKG 1
Rate: approx 75/min
Rhythm: Baseline sinus rhythm, P:QRS is 1:1
Axis: Physiologic
Injury: ST elevation is present in the anterior, septal, and literal leads. Massive ST segment elevation is present in V2-V6, with moderate ST elevation that obscures visualization of the QRS complex in lead one. Changes are consistent with LCA occlusion. Other: R wave progression is difficult to determine secondary to the pathological ST-T changes. No evidence of chamber enlargement or hypertrophy.
Interpretation EKG 2
The EKG reveals an atrial flutter at a rate of approx 100 per minute. The QRS complexes are narrow and reveal a physiological axis. There is evidence of a premature ventricular complex, readily identifiable in the lateral chest leads. No evidence of ischemia or infarction. No evidence of R or L bundle branch block. Atrial flutter is conducted at approx 3:1. (3 flutter waves to one QRS).
Interpretation EKG 3
The EKG reveals an irregularly irregular rhythm suggestive of atrial fibrillation. The rate is variable, with a controlled or slow ventricular response. The axis is physiologic. ST-T changes suggestive of ischemia/injury are present in leads II, III, and aVF. ST elevation of >1mm in limb leads is indicative of a possible inferior wall myocardial infarction. Reciprocal changes are seen in leads one and aVL. Early R wave progression.
For Complete presentation: EKG INTERPRETATION
by
Akshaya Srikanth
Hyderabad, India
Rate: approx 75/min
Rhythm: Baseline sinus rhythm, P:QRS is 1:1
Axis: Physiologic
Injury: ST elevation is present in the anterior, septal, and literal leads. Massive ST segment elevation is present in V2-V6, with moderate ST elevation that obscures visualization of the QRS complex in lead one. Changes are consistent with LCA occlusion. Other: R wave progression is difficult to determine secondary to the pathological ST-T changes. No evidence of chamber enlargement or hypertrophy.
Interpretation EKG 2
The EKG reveals an atrial flutter at a rate of approx 100 per minute. The QRS complexes are narrow and reveal a physiological axis. There is evidence of a premature ventricular complex, readily identifiable in the lateral chest leads. No evidence of ischemia or infarction. No evidence of R or L bundle branch block. Atrial flutter is conducted at approx 3:1. (3 flutter waves to one QRS).
Interpretation EKG 3
The EKG reveals an irregularly irregular rhythm suggestive of atrial fibrillation. The rate is variable, with a controlled or slow ventricular response. The axis is physiologic. ST-T changes suggestive of ischemia/injury are present in leads II, III, and aVF. ST elevation of >1mm in limb leads is indicative of a possible inferior wall myocardial infarction. Reciprocal changes are seen in leads one and aVL. Early R wave progression.
For Complete presentation: EKG INTERPRETATION
by
Akshaya Srikanth
Hyderabad, India